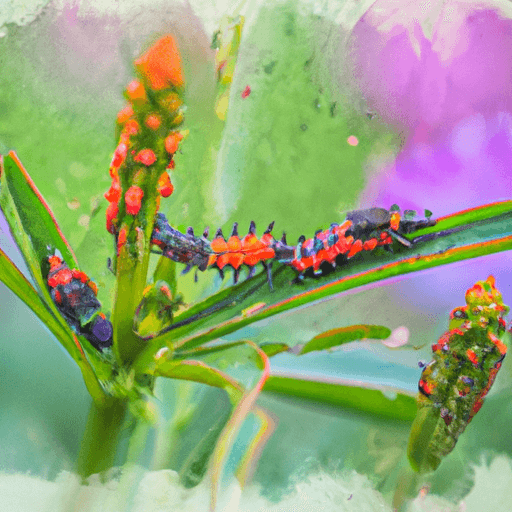Ladybug larvae are valuable companions in the garden, aiding in the control of pest populations. These beneficial insects undergo a complete metamorphosis, progressing from eggs to larvae and pupae before reaching adulthood. Development takes around six weeks for sevenspotted lady beetles, during which larvae molt four times.
With elongated, spiny bodies and distinctive black coloration adorned with red, orange, or white markings, these voracious eaters feast on pest insects like aphids, scale, thrips, and mites.
To foster their presence, one should provide ample food sources, eschew harmful insecticides, offer water, and even consider purchasing ladybugs to bolster their population.
Life Stages of Ladybugs
Ladybugs go through a complete metamorphosis, with their life stages including eggs, larvae, pupae, and adults.
The larvae stage of ladybugs is particularly important in natural pest control and plays a crucial role in garden ecosystems. Ladybug larvae are voracious eaters and consume a wide range of pest insects, including aphids, soft scale, whitefly pupa, thrips, and spider mites. In fact, they can devour about 400 aphids in just three weeks.
Ladybug larvae also feed on pollen, making them beneficial pollinators as well. By preying on these pests, ladybug larvae help to maintain a balance in garden ecosystems and reduce the need for chemical insecticides.
Providing sufficient food sources and avoiding the use of harmful insecticides can help protect and encourage ladybug larvae in your garden.
Appearance of Ladybug Larvae
With an elongated, spiny body and black coloration accented by red, orange, or white markings, the larvae of these insects spend several weeks consuming pest insects.
Ladybug larvae are highly efficient natural pest control agents in gardens. They have a voracious appetite and can consume up to 400 aphids in just three weeks. Additionally, ladybug larvae prey on soft scale, whitefly pupa, thrips, and spider mites, making them valuable allies in the garden.
By attracting ladybugs to your garden, you can benefit from their pest control abilities and reduce the need for harmful insecticides. Planting their favorite flowers, which also serve as a source of pollen, can help attract ladybugs.
Creating a suitable habitat with sufficient food sources and water can further protect ladybug larvae and support their population growth.
Ladybug Nymphs
The immature stage of these insects, sometimes referred to as nymphs, undergoes a simple metamorphosis and has a distinct appearance from adult ladybugs. Ladybug nymphs go through a process of differentiation and growth during their development. As they molt, their bodies change and become more similar to adult ladybugs.
Ladybug nymphs have a voracious predatory behavior, feeding on a wide range of pest insects such as aphids, soft scale, whitefly pupa, thrips, and spider mites. They are particularly effective in controlling aphid populations, consuming about 400 aphids in just three weeks. Ladybug nymphs also feed on pollen, which can be an additional food source for them.
It is important to protect ladybug nymphs by providing sufficient food sources, avoiding the use of harmful insecticides, and offering a source of water in the garden.
Favorite Foods of Ladybug Larvae
Ladybug larvae have a voracious appetite and can consume up to 400 aphids in just three weeks. This makes them valuable allies in the garden for natural pest control.
Here are three ways to attract ladybugs and ensure their presence for pest control:
-
Plant Their Favorite Flowers: Ladybugs are attracted to flowers such as dill, fennel, yarrow, and marigold. These plants provide nectar and pollen, which are important food sources for adult ladybugs.
-
Avoid Harmful Insecticides: Ladybugs are sensitive to insecticides, so it’s important to use natural pest control methods that won’t harm them or their prey. This includes using organic pesticides or beneficial insects like ladybugs themselves.
-
Provide Water Sources: Ladybugs need water to survive, so providing a shallow saucer filled with water can attract them to your garden. Just make sure to change the water often to prevent mosquito breeding.
Protecting Ladybug Larvae
Providing sufficient food sources and avoiding harmful insecticides are important steps in protecting the development and survival of ladybug larvae.
Ladybug larvae serve as natural pest control in gardens, as they consume large numbers of aphids, soft scale, whitefly pupa, thrips, and spider mites. By attracting ladybugs to your garden, you can benefit from their voracious appetite for these pests.
Planting their favorite flowers, such as daisies, marigolds, and yarrow, can help attract ladybugs. Additionally, avoiding the use of insecticides is crucial, as these chemicals can harm ladybugs and their prey.
Instead, opt for organic pest control methods, such as introducing beneficial insects or using companion planting techniques.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does It Take for Ladybug Larvae to Hatch From Their Eggs?
Ladybug larvae typically hatch from their eggs in about 3 to 5 days. The optimal temperature for their development is around 70 to 80 degrees Fahrenheit.
What Is the Average Lifespan of an Adult Ladybug?
The average lifespan of an adult ladybug is about one year. Ladybugs go through a complete metamorphosis, including the stages of eggs, larvae, pupae, and adults. The development from eggs to adults takes around six weeks for sevenspotted lady beetles.
Are All Ladybug Larvae Black With Red, Orange, or White Markings, or Are There Other Color Variations?
Ladybug larvae, natural predators, go through stages of development. While most are black with red, orange, or white markings, there can be other color variations. They play a crucial role in controlling pest populations in gardens.
Do Ladybug Larvae Have Any Predators Besides Humans?
Ladybug larvae have predators such as birds, spiders, and other insects. However, they play a crucial role in pest control by consuming aphids, scale insects, thrips, and spider mites, helping to keep garden populations in check.
Can Ladybug Larvae Be Harmful to Plants or Gardens in Any Way?
Ladybug larvae are not harmful to plants or gardens. In fact, they are beneficial for plant health. They feed on pests like aphids, scale, thrips, and spider mites, helping to control their populations naturally.